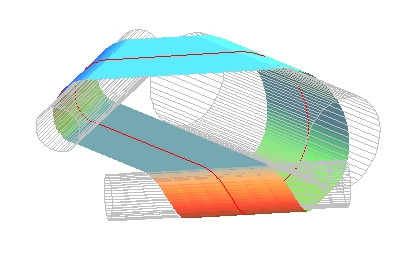
 parag. 1
parag. 1
 parag. 2
parag. 2
Ruban de Mobius fait de parties cylindriques et planes
Programme réalisé suite à l'envoi par Robert Ferréol d'un article allemand sur la réalisation d'un ruban de Mobius avec trois cylindres comme dans le paragraphe 1.
(voir le site de Ferréol : http://www.mathcurve.com/surfaces/mobius/mobius.shtml)
Télécharger l'article allemand : l'article "zippé"
J'ai fait pour trois cylindres puis généralisé ... puis j'ai pensé faire un ruban plus symétrique d'où le cas 2.
Le code Maple ci-dessous a été un peu modifié depuis : télécharger le fichier Maple mis à jour
ICI

RUBAN1(4,7,1,3);
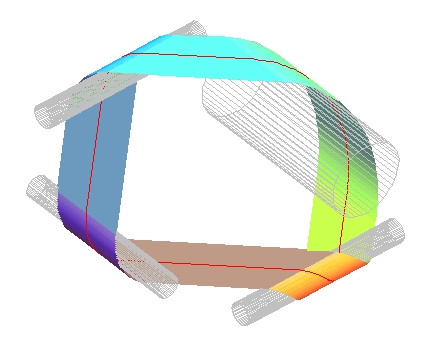
RUBAN1(5,9,1,3);
 Début
Début
II. Ruban régulier à n (n>2) demi-tours ( n cylindres égaux)
Cylindres d'axes ni // ni ortho. à Oz, déduits par rotations d'axe Oz de 2*Pi/n.
restart: with(plots):
rotOz:=(M,u) -> [M[1]*cos(u)-M[2]*sin(u),M[1]*sin(u)+M[2]*cos(u),M[3]]:
rotOx:=(M,u) -> [M[1],M[2]*cos(u)-M[3]*sin(u),M[2]*sin(u)+M[3]*cos(u)]:
dir:=t ->[cos(t),sin(t),0]:
pv:= (U,V) -> simplify([U[2]*V[3]-U[3]*V[2],U[3]*V[1]-U[1]*V[3],U[1]*V[2]-U[2]*V[1]]):
ps:= (U,V) -> simplify(add(U[i]*V[i],i=1..nops(U))):
norme:= V -> sqrt(V[1]^2+V[2]^2+V[3]^2):
# *****************************************
# --------- les paramètres ---------
# n ----> nombre de cylindres
# a ----> inclinaison cylindres
# d ----> distance des axes à Oz (augmenter si croisements aux jonctions)
# large ----> largeur bande
# vue ----> angle de vue
# afcyl = 0 si pas afficher les cylindres, 1 si oui
# *****************************************
RUBAN := proc(n,a,d,large,vue, afcyl)
local k,theta,gene,cercle,base0,cyl,deb,fin,axebase0,hel,axebase1,perpcom1,perpcom,
tg0,tg1,CYLS,HELS,RACS,RubH,RubR,i,col,solx,t0,r,x,pcdist,u,liste:
k:=sqrt(n)*large/sin(theta/2): # longueur cylindre
theta:=2*Pi/n:
gene[0]:=rotOx([0,1,0],a):
axebase0:=rotOx([-d,u,0],a):
cercle:=[-d+ r*cos(t),0,r*sin(t)]:
base0:=rotOx(cercle,a):
cyl[0]:=expand(subs(r=r-0.05*r,base0)+ u*gene[0]): # ***** rayon + petit
for i from 1 to n-1 do
gene[i]:=rotOz(gene[0],i*theta);
cyl[i]:=rotOz(cyl[0],i*theta); od:
axebase1:=rotOz(axebase0,theta):
perpcom1:=pv(gene[0],gene[1]):
perpcom:=expand(perpcom1/norme(perpcom1)):
pcdist:=simplify(ps( subs(u=0,axebase0)-subs(u=0,axebase1), perpcom)):
r:=abs(pcdist/2):
t0:=Pi-arccos(sin(a)*sin(Pi/n)/(cos(a)^2*cos(Pi/n)^2+1-cos(a)^2)^(1/2)):
hel[0]:=rotOx([-d- r*cos(t),X*t,r*sin(t)],a):
for i from 1 to n-1 do hel[i]:=rotOz(hel[0],i*theta): od:
tg0:=subs(t=t0,diff(hel[0],t)): tg1:=subs(t=-t0,diff(hel[1],t)):
col:=simplify(pv(tg0,tg1)):
solx:=simplify([solve(evalf(norme(col)^2),X)]):
solx:=map( w -> Re(w),solx):# pour n=5 il y a un I*upsilon
# evalf mis à solx mais réponses ordre différent
x:=min(seq(solx[i],i=1..nops(solx))):
for i from 0 to n-1 do deb[i]:=subs(t=-t0,X=x,hel[i]); fin[i]:=subs(t=t0,X=x,hel[i]); od:
CYLS:=seq(plot3d(cyl[i],t=0..2*Pi,u=-k..k,style=LINE,color=grey,grid=[20,2]),i=0..n-1):
HELS:=seq(spacecurve(subs(X=x,hel[i]),t=-t0..t0,thickness=2,color=red),i=0..n-1):
RACS:= seq(spacecurve(subs(x=x,[fin[i],deb[(i+1) mod n]]),thickness=2,color=red),i=0..n-1):
RubH:=seq(plot3d(subs(X=x,expand(hel[i]+u*(gene[i]))),t=-t0..t0,u=-large..large,grid=[40,2],
style=patchnogrid),i=0..n-1):
RubR:=seq(plot3d(expand(fin[i]+u*gene[i]+t*(deb[(i+1) mod n]+
u*(-gene[(i+1) mod n]-gene[i])-fin[i])),
u=-large..large,t=0..1,grid=[2,20], style=patchnogrid),i=0..n-1):
if afcyl=0 then liste :=[HELS,RACS,RubH,RubR ] else liste:=[CYLS,HELS,RACS,RubH,RubR ] fi:
print(display(liste,scaling=constrained,orientation=[60,vue],lightmodel=light2));
end:
#plotsetup(window);
#plotsetup(inline);
#plotsetup(gif,plotouput="c:\ruban3vue1.gif",plotoptions="width=400, height=400"):
# ************ les paramètres ***********************
# ======= RUBAN := proc(n,a,d,large,vue,afcyl) ======
# n ----> nombre de cylindres
# a ----> inclinaison cylindres
# d ----> distance des axes à Oz
# (augmenter d si chevauchements aux jonctions)
# large ----> largeur bande
# vue ----> angle de vue
# afcyl = 0 si pas afficher les cylindres, 1 si oui
# ***************************************************
plotsetup(inline); ang:=Pi/20: RUBAN(3,ang,9,5,0,1); RUBAN(3,ang,9,5,60,0);
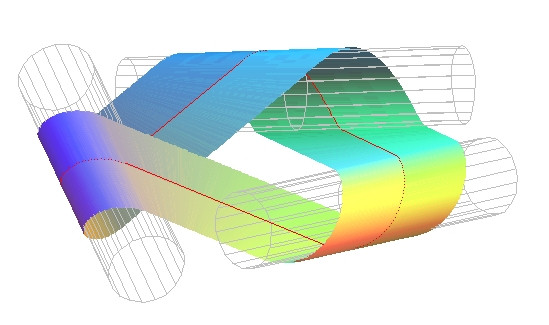
# si ang -> 0, on tend vers le "ruban pliage" du site de R. Ferréol
plotsetup(inline); ang:=Pi/50: RUBAN(3,ang,9,6,0,1); RUBAN(3,ang,9,6,60,0);
-egaux.jpg)
plotsetup(inline); RUBAN(4,evalf(Pi/9),13,4,0,1); RUBAN(4,Pi/9,13,4,50,0);
plotsetup(window); RUBAN(5,evalf(Pi/10),25,4,0,1); RUBAN(5,evalf(Pi/10),25,4,50,0);
plotsetup(window); RUBAN(6,Pi/12,28,4,0,1); RUBAN(6,Pi/12,28,4,50,0);
 Début
Début